Electrical Schematics | How to Interpret | Beginner’s Guide
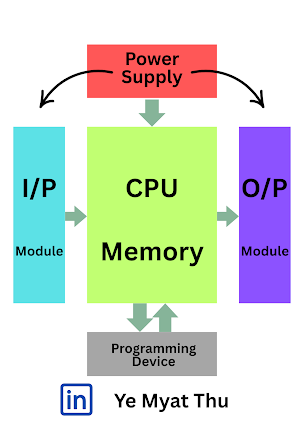
Understanding electrical schematics is a foundational skill for anyone working in electrical, instrumentation, control, or automation (EICA). Whether you're troubleshooting a machine, designing a panel, or programming a PLC, the ability to read and interpret these diagrams is essential. What Is an Electrical Schematic? Schematic Diagram – Shows the functional connections (used for troubleshooting and design). Wiring Diagram – Shows physical connections, cable routing, and terminal numbers. Single-Line Diagram (SLD) – Simplified view, mostly for power distribution. P&ID (for instrumentation) – Shows process, piping, instruments, and control systems. Step-by-Step: How to Read a Schematic 1. Understand the Layout Schematics usually flow left to right or top to bottom . Power supply is often on the left or top. Loads (motors, solenoids, relays) are placed on the right or bottom. 2. Learn the Symbols You’ll need to recognize IEC or ANSI symbols for: Power sources (batteries...